Moderna Therapeutics, a biotech company based in Cambridge, Mass., has shipped the first batches of its COVID-19 vaccine. The vaccine was created just 42 days after the genetic sequence of the COVID_19 virus, called SARS-CoV-2, was released by Chinese researchers in mid-January.
COVID-19 Vaccine Developed and Clinical Trials Have Begun
NIH scientists also began testing an antiviral drug called remdesivir that had been developed for Ebola, on a patient infected with SARS-CoV-2. The trial is the first to test a drug for treating COVID-19, and will be led by a team at the University of Nebraska Medical Center. The first patient to volunteer for the ground-breaking study is a passenger who was brought back to the US after testing positive for the disease aboard the Diamond Princess. Others diagnosed with COVID-19 who have been hospitalised will also be part of the study.
Remdesivir showed encouraging results among animals infected with two related corona viruses, one responsible for severe acute respiratory syndrome (SARS) and another for causing Middle East respiratory syndrome (MERS). Volunteers will be randomly assigned to receive either the drug or a placebo intravenously for 10 days, and they will have blood tests and nose and throat swabs taken every two days to track the amount of virus in their bodies. Even if the drug shows some efficacy in keeping blood levels of SARS-CoV-2 from growing, it could help to contain spread of the infection.
Moderna’s vaccine against COVID-19 was developed in record time because it’s based on a relatively new genetic method that does not require growing huge amounts of virus. Instead, the vaccine is packed with mRNA, the genetic material that comes from DNA and makes proteins. Moderna loads its vaccine with mRNA that codes for the right corona virus proteins which then get injected into the body. Immune cells in the lymph nodes can process that mRNA and start making the protein in just the right way for other immune cells to recognise and mark them for destruction.
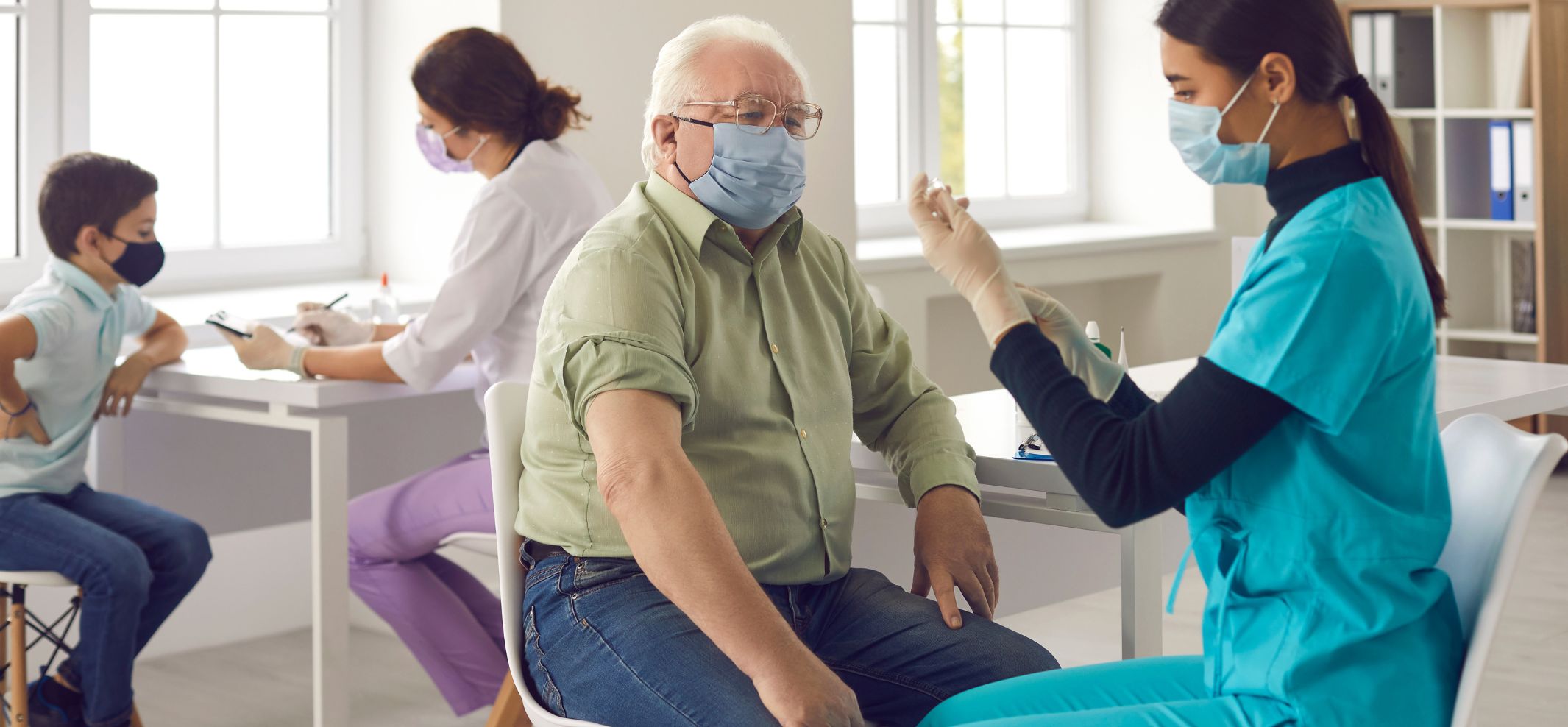
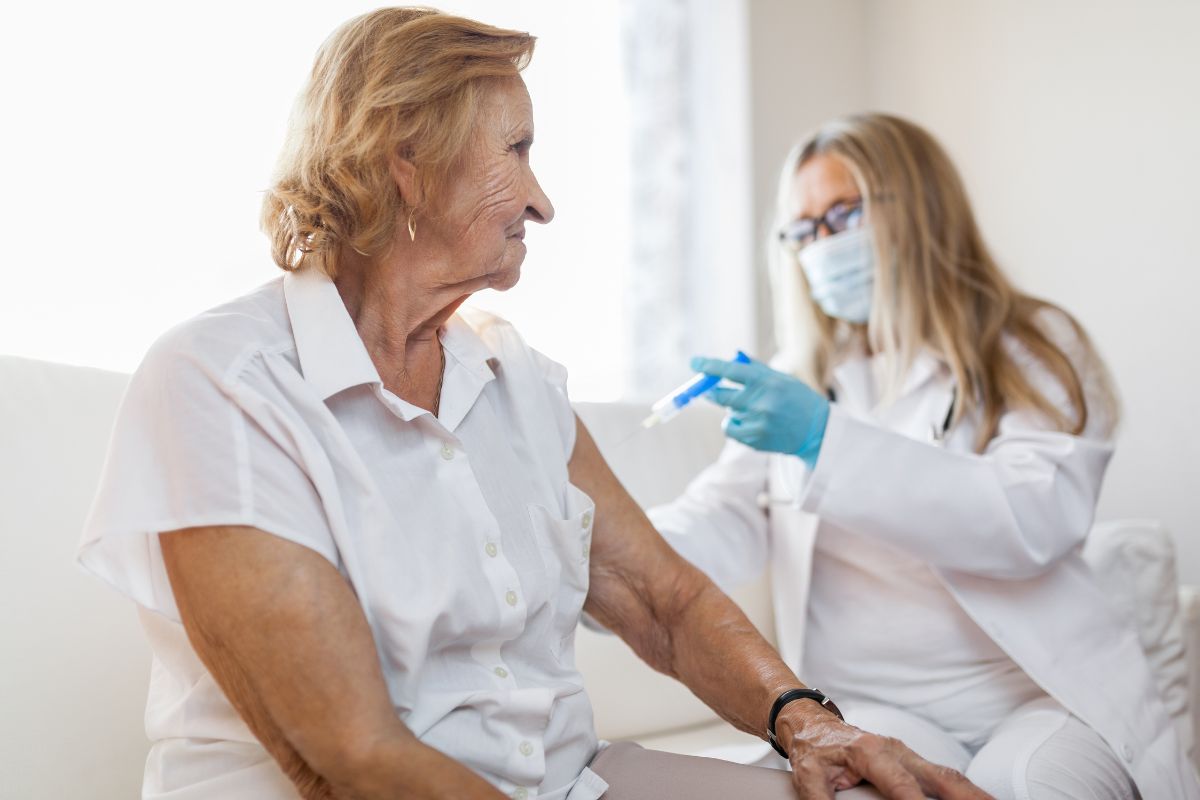
First dose to be delivered Monday in clinical trial for potential COVID-19 vaccine
A clinical trial evaluating a vaccine designed to protect against the new corona virus will begin Monday, according to a government official. The first participant in the trial will receive the experimental vaccine on Monday, the official said, speaking on the condition of anonymity because the trial has not been publicly announced yet. The National Institutes of Health is funding the trial, which is taking place at the Kaiser Permanente Washington Health Research Institute in Seattle, the official said.
Public health officials say it will take a year to 18 months to fully validate any potential vaccine.
Testing will begin with 45 young, healthy volunteers with different doses of shots co-developed by NIH and Moderna Inc. There’s no chance participants could get infected from the shots, because they don’t contain the virus itself. The goal is purely to check that the vaccines show no worrisome side effects, setting the stage for larger tests.
Dozens of research groups around the world are racing to create a vaccine as COVID-19 cases continue to grow. Importantly, they’re pursuing different types of vaccines — shots developed from new technologies that not only are faster to produce than traditional inoculations but might prove more potent. Some researchers even aim for temporary vaccines, such as shots that might guard people’s health a month or two at a time while longer-lasting protection is developed.
Sources:
- https://time.com/5790545/first-covid-19-vaccine/
- https://www.fox29.com/news/first-dose-to-be-delivered-monday-in-clinical-trial-for-potential-covid-19-vaccine