The impact of technology on hospital services
Share
The healthcare industry has undergone massive technological transformations in recent decades. From electronic health records to telemedicine, innovations are changing how hospitals deliver care and operate behind the scenes. While technology holds great promise for improving hospital services, it also brings new challenges that must be addressed thoughtfully.
Monitoring Patients in the ICU
One area seeing rapid innovation is patient monitoring in settings like the intensive care unit (ICU). New wearable devices and wireless sensors now allow continuous monitoring of vital signs like heart rate, breathing rate, and blood oxygen levels. Streaming this data to providers’ smartphones and computers helps them detect emerging problems sooner. For example, early signs of sepsis, a life-threatening immune response, can now be spotted hours or days sooner than with intermittent check-ins. This allows earlier intervention in the ICU, giving patients a better chance of recovery.
Electronic Health Records (EHR) Integration
One of the most notable advancements is the integration of electronic health records (EHR) systems. Gone are the days of cumbersome paper-based files. Now patient information is digitized and accessible with just a few clicks. EHR systems enable healthcare providers to access comprehensive patient histories instantly, facilitating more informed decision-making and coordinated care. This seamless exchange of information among departments within a hospital and even across healthcare networks enhances communication and reduces the likelihood of errors.
Telehealth and Telemedicine
Telehealth and telemedicine platforms are also transforming hospital care. These technologies allow physicians to consult with patients remotely, coordinate care between visits, and conduct rounds without being physically present. Not only does this improve patient access and convenience, but it also optimizes doctors’ time and enables care teams to collaborate easily. For hospitals facing provider shortages or serving large rural populations over wide geographic areas, telemedicine is making high-quality care more accessible.
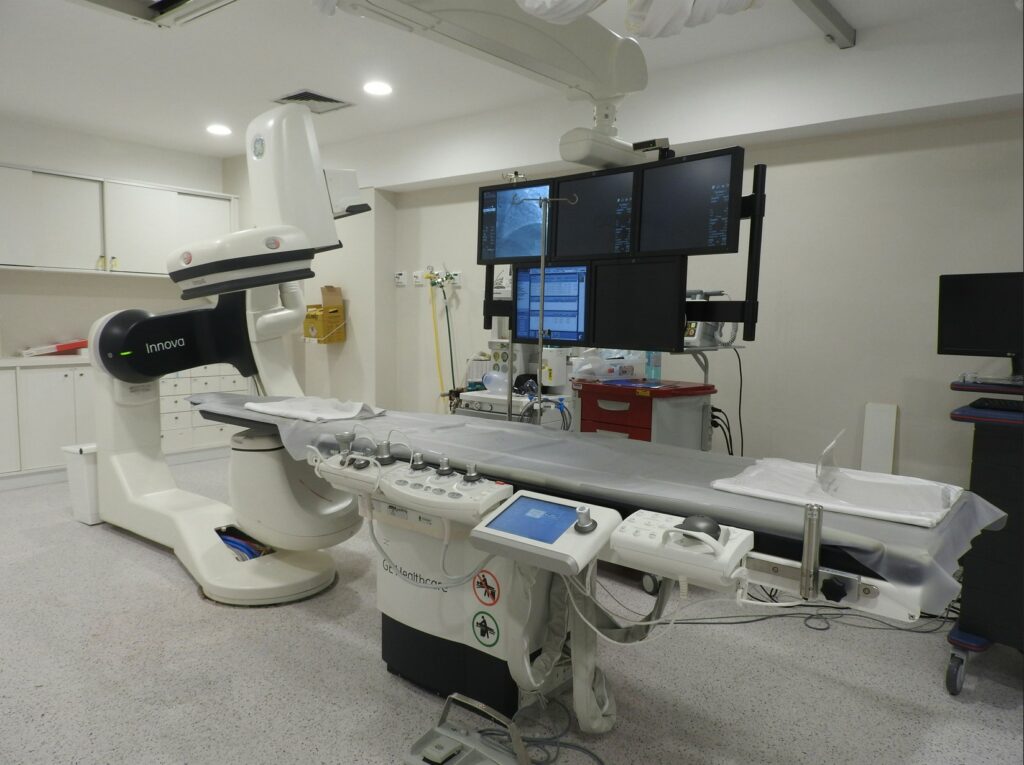
Photo by sandro porfirio on Unsplash
AI Assistance
Artificial intelligence (AI) algorithms are beginning to assist doctors by analyzing scans, lab results, and notes buried in medical records. This helps surface insights that overloaded human providers may miss, like early signs of disease or complications. However, physicians must be very prudent in using AI tools, given some algorithms’ ‘black box’ nature. Doctors should view AI as a supplementary input to clinical decision-making rather than a wholesale replacement for their expertise. AI also shows promise for improving hospital operational efficiency by optimizing scheduling and inventory management.
Administrative Technologies
Behind the scenes, hospitals rely on all manner of technology to coordinate complex care. Electronic health records centralize patient information and treatment histories, avoiding dangerous mistakes from fragmented paper charts. Inventory management programs track supplies, equipment, and pharmaceuticals to ensure items are well-stocked. Scheduling systems allow efficient booking of operating rooms, beds, and various services at the hospital. While not directly touching patients, these technologies are mission-critical for safe and efficient hospital operations.
Advanced Diagnostic Procedures
Furthermore, technology has revolutionized diagnostic procedures, leading to quicker and more accurate diagnoses. Advanced imaging techniques—such as MRI, CT scans, and ultrasound—have become indispensable medical tools. These imaging modalities provide detailed insights into the patient’s condition, allowing for early detection and precise treatment planning. In critical care settings, such as the ICU, where timely interventions can be a matter of life and death—technology is crucial in monitoring patients’ vital signs and detecting subtle changes in real time.
Medication Management and Administration
Another area where technology has made significant strides is in medication management and administration. Automated dispensing systems and barcode medication administration (BCMA) have streamlined the medication process, reducing the risk of errors and ensuring patients receive the right medication at the right dose and time. Smart infusion pumps with safety features also help prevent medication errors and adverse drug reactions, improving patient safety and outcomes.
Precision Surgery and Minimally Invasive Procedures
In surgery, technology has ushered in a new era of precision and minimally invasive procedures. Robotic-assisted surgery systems allow surgeons to perform complex operations with enhanced skill and precision, leading to shorter recovery times and reduced patient complications. Furthermore, advancements in surgical imaging techniques, such as intraoperative MRI and fluoroscopy, provide real-time guidance during procedures, enhancing surgical outcomes and patient safety.
Patient Engagement and Empowerment
Moreover, technology has revolutionized patient engagement and empowerment through patient portals and mobile health applications. These platforms allow patients to access their medical records, schedule appointments, communicate with healthcare providers, and monitor their health metrics remotely. By empowering patients to take an active role in their healthcare journey, technology fosters greater accountability and adherence to treatment plans, ultimately improving health outcomes.
Medical Devices
Cutting-edge medical devices like 3D printers, robotic surgeons, and image-guided therapy systems allow hospitals to offer highly complex procedures. 3D printing creates customized implants, prosthetics, and anatomical models for presurgical planning. Robotic surgery allows greater precision, smaller incisions, and faster recovery times. Image-guided technology lets surgeons visualize internal anatomy during minimally invasive procedures. Patients benefit from better outcomes with these advanced devices.
Challenges of New Technology
Of course, new technology also poses challenges. Protecting patient privacy is paramount, especially with digitized records that are highly vulnerable to hacking. The speed of innovation also risks outpacing adequate testing, regulation, and staff training on new tools before implementation. Over-automation threatens to undermine human relationships between patients, nurses, and doctors, essential to compassionate care.
There are also important ethical questions about how technology impacts hospital accessibility and affordability. Often, the latest innovations debut at well-resourced major hospitals before spreading more widely. This worsens disparities if lower-income and rural hospitals cannot afford the significant investments required. Policymakers must consider funding and incentive structures to ensure advanced technologies that improve hospital services are available equitably, not just to the privileged few.
Final Thoughts
The impact of technology on hospital services is undeniable. Technology has transformed healthcare delivery, from enhancing diagnostic accuracy and treatment efficacy to improving patient safety and engagement. Hospitals must adapt and evolve to leverage these advancements as we continue to embrace technological innovations. By harnessing the power of technology, hospitals can optimize their services, ultimately leading to better patient outcomes and a healthier society.




Upcoming Events
6th Annual Aged Care Week
June 18, 2025
Subscribe
We send emails,
but we do not spam
Join our mailing list to be on the front lines of healthcare , get exclusive content, and promos.